NXE Set to Capitalise on Vanadium Demand as it Fast Tracks Mine Development
Published 25-OCT-2018 10:27 A.M.
|
12 minute read
Hey! Looks like you have stumbled on the section of our website where we have archived articles from our old business model.
In 2019 the original founding team returned to run Next Investors, we changed our business model to only write about stocks we carefully research and are invested in for the long term.
The below articles were written under our previous business model. We have kept these articles online here for your reference.
Our new mission is to build a high performing ASX micro cap investment portfolio and share our research, analysis and investment strategy with our readers.
Click Here to View Latest Articles
The long term demand for vanadium is a story that’s been well told. Like that of other new age battery metals, vanadium demand will benefit as we shift to sustainable energy sources and rechargeable batteries.
Already, vanadium has a solid position in the battery metals story, being the critical ingredient in grid scale vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFB). In light of this, there’s a compelling long term argument for vanadium demand, but what’s less well known is that short-term demand-supply fundamentals are also heavily on the side of higher prices.
Vanadium is the most common additive in high strength rebar, as it offers the best combination of high strength, good ductility, bendability, weldability, and reduced sensitivity to strain ageing.
With these attributes in mind, vanadium demand is set to be given a huge boost from November 1 — the date when China will enforce new steel rebar standards to cut down on substandard steels in the country and improve build quality in the country’s construction industry.
Already, this new legislation is creating tightness in the market. Prices are nearing US$31.50/lb ($69,426/tonne), up from less than US$10/lb this time last year, and have been accelerating since September, rising by almost 2% per day.
Going forward, car makers will increasingly incorporate vanadium into their vehicles to reduce their weight and improve fuel efficiency.
Clearly there are a number of converging factors at play, not least the development of renewable energy as we move away from traditional fossil fuels.
New Energy Minerals (ASX:NXE) is seeking to capitalise on this rising demand for vanadium with a focus on the exploration and mining of vanadium as well as graphite — critical commodities that make the rapidly growing market of energy storage and electric vehicle transportation possible.
While in the past the company had a more diversified asset portfolio, this has now been narrowed down with its energy all being directed to the development of the Caula Vanadium-Graphite Project in Northern Mozambique.
The company has been intent on fast-tracking the development of the mine and the results are in from and independent Scoping Study that was undertaken in October.
The study pointed to Caula generating significant financial returns through a two-phase development schedule for an open pit vanadium and graphite mining operation.
The economics are very encouraging, showing a A$929 million NPV and 78% IRR calculated using very conservative vanadium and graphite prices.
The study found the project to be technically and financially viable with no immediate or obvious impediments to mining, and having an outstanding life of mine strip ratio of 1:1, with a large high grade JORC Measured Resource and simple fully integrated process flowsheet design (using flotation and magnetic separation) to extract graphite and vanadium.
Led by a highly experienced board and management team with a 15-year track record of investment and successful project development in Mozambique and Africa, NXE aim to become a key provider of vanadium and graphite, both key components used in battery production.
All the latest from newly re-named,

Formerly known as Mustang Resources (ASX:MUS), the company’s new name, New Energy Minerals (ASX:NXE), approved by shareholders on October 2, better reflects the company's focus on the critical commodities of vanadium and graphite.
The company’s highly prospective Caula Vanadium-Graphite Project consists of two exploration licenses totalling more than 16,790ha in Mozambique — one of the fastest growing economies in Africa. Notably, the Caula Project is located along strike from the world class $580 million-capped Syrah Resources Ltd’s (ASX:SYR) Balama Project.
SYR’s Balama Project contains a combined Proved and Probable Reserve of 81.4Mt at an average grade of 16.2% TGC. Here you can see NXE’s Caula Project and Syrah resources’ nearby mine, amongst others.
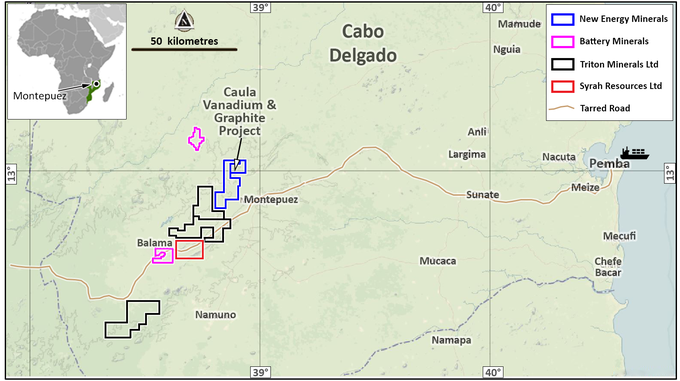
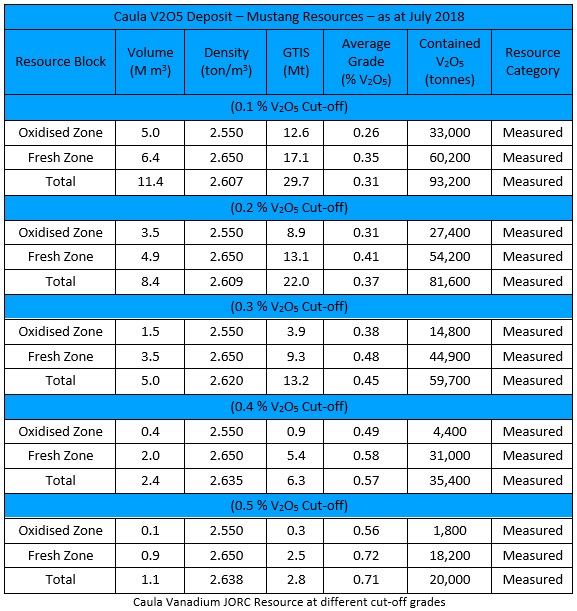
In July 2018, NXE announced a maiden vanadium mica-hosted 1 JORC Measured Resource for Caula of 22Mt at 0.37% V2O5 for 81,600 tonnes of contained vanadium pentoxide.
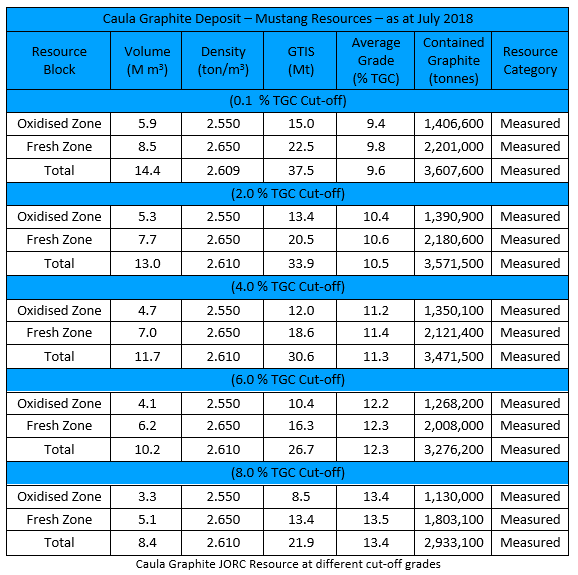
The company concurrently announced a 317% increase in its JORC Graphite Resource to 21.9Mt at 13.4% Total Graphitic Carbon (TGC) (8% cut-off), for a total of 2,933,100 tonnes of contained Graphite, all in the measured category.
Independent Scoping Study
The results of the Scoping Study indicate the potential to generate significant financial returns through a two-phase development schedule for an open pit vanadium and graphite mining operation at the Caula deposit.
The independent Scoping Study, undertaken in June by Bara International, examined all facets of geology, mining, processing and supporting infrastructure and included a site visit by the consultants.
Bara found the project to be technically and financially viable with no immediate or obvious impediments to mining, and having an outstanding life of mine strip ratio of 1:1.
The economics are very encouraging, showing a A$929 million NPV and 78% IRR using only conservative vanadium and graphite prices in the model. The study assumed vanadium price of $18/lb, while vanadium is now trading at ~$30/lb.
The table below outlines the key outcomes of Phase 1 and 2:
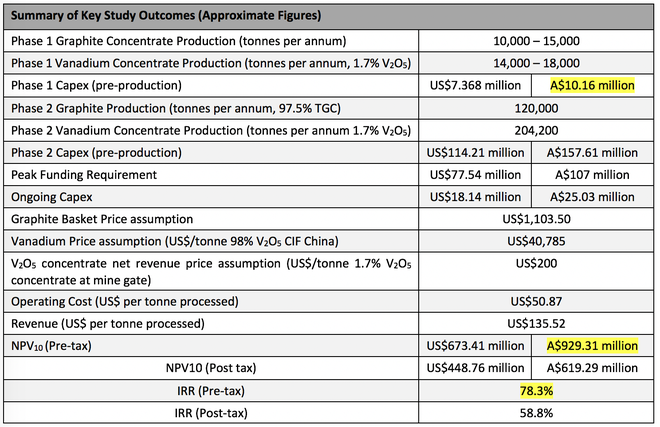
Phase 1 Key study outcomes:
- Pre-production capex of approximately US$7.36 million (A$10.16M).
- Mine production rate of approximately 120,000 tonnes per annum over two years.
- Estimated annual production of approximately 10,000 to 15,000 tonnes of graphite concentrates and 14,000 to 18,000 tonnes of vanadium concentrates over two years.
- Generating approximately US$16 million (A$22M) total EBITDA over first 2 years with Phase 2 commissioned in Year 3.
Additional key outcomes of the study for Phase 2 — the development of an open pit vanadium and graphite mining operation — are as follows:
- Pre-production capex of approximately US$114 million (A$157 million) with construction scheduled to commence in year two of Phase 1.
- Estimated mine production rate of 1.5 Mtpa.
- Estimated annual production of approximately 120,000 tonnes of graphite concentrates and approximately 204,200 tonnes of vanadium concentrate (1.7% V2O5 flake) per year over 24 years.
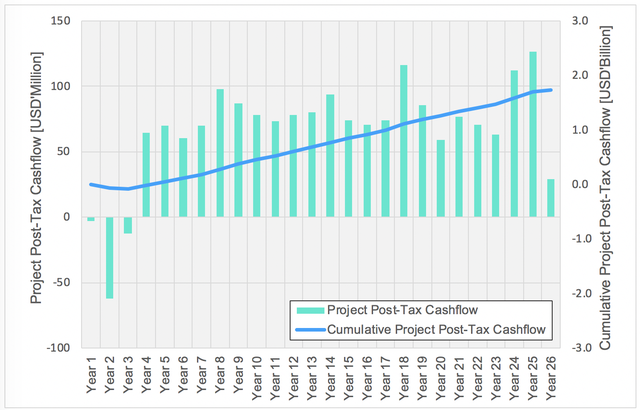
This low capital cost of just $10 million to get underway means development the project can begin quickly. Phase 2 will then require US$77 million of outside funds. Total project post-tax payback is less than four years from start of phase 1.
The project cashflow analysis, as illustrated below, determined that the project is profitable from year four on, and the payback period is four years from the start of Phase 1.
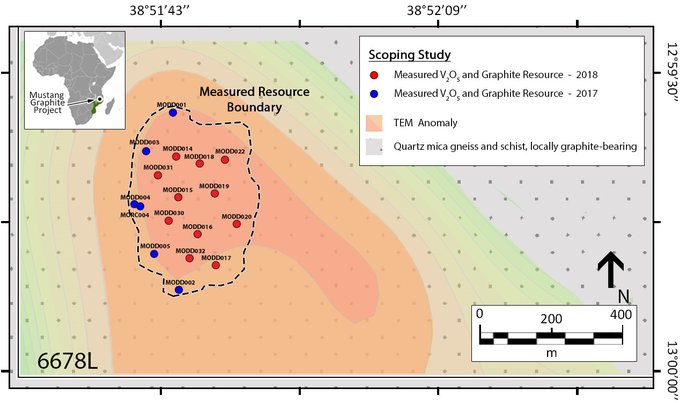
Here are the locations of drillholes and the plan view of mineralisation of 2018 Graphite and V2O5 Resource.
As part of the study, Bara identified the additional metallurgical test work to be undertaken. This includes optimising graphite grinding and flotation; further vanadium concentration test work; optimisation of vanadium concentrate grade; vanadium roast and leach test work; and geochemical, mechanical and rheological testwork on tailings materials to support designs for deposition methods and facility lining requirements.
Given that the Caula Mineral Resource is already all in the JORC Measured category, Bara determined that these tasks can be commenced on short notice and can soon advance to the next level of study in the short term.
Further studies are being undertaken and results will be made available in the coming months as NXE moves towards the low cost Phase 1 pilot plant targeted for production by the first half of 2019 and the concurrent completion of definitive feasibility studies and development activities required for Phase 2.
Note that the PFS will also incorporate the vanadium roaster (refinery), which will boost economics even further as it’s NXE’s express intention to produce >98% purity vanadium products.
Vanadium outlook
New steel rebar regulations are set to come into force in China in November after being announced by the Standardization Administration of China (SAC) on February 6. The SAC also introduced a special action to cut down on substandard steels in the country.
China currently produces about 200 million MT of rebar annually, with typical vanadium content in Grade 3 rebar coming in at 0.3 kilograms per MT of steel.
Vanadium is used as a strengthening agent in steel, and China’s new rebar regulations are aimed at ensuring that newly built homes will be more resistant to earthquakes.
Market watchers told Metal Bulletin that rebar prices are likely to rise after the new regulations come into effect, as production costs will increase by $16 to $24 per tonne
SAC’s high-strength rebar standard, which eliminates low-strength Grade 2 (335MPa) rebar and authorises three different high-strength standards: Grade 3 (400MPa), Grade 4 (500MPa) and Grade 5 (600MPa).
John Hilbert of Vanitec called the new standard a positive development towards the increased consumption of the metal. “Vanadium is the most common addition for high strength rebar, because it offers the best combination of high strength, good ductility, bendability, weldability, and reduced sensitivity to strain aging,” he said.
Vanadium has emerged as an essential metal in the current climate centred around the development of renewable energy as society continues to shift away from traditional fossil fuels. In May of this year, the US Department of Energy made a $30 Million funding commitment to long-term battery solutions through its Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) office.
Additionally, more and more automobile manufacturers are incorporating vanadium into vehicles in order to reduce their weight and increase fuel efficiency as regulations continue to become stricter in the realm of fuel economy. The rising demand has been extremely beneficial to those in the mining business of vanadium. The metal’s application to battery production is another factor influencing its current growth.
Graphite
Like vanadium, the outlook for graphite is working in favour of NXE too. The below article from Finfeed.com takes a closer look at graphite and graphite prices. To summarise, the supply of graphite is tightening, while the demand is forecast to ‘skyrocket’.
When it comes to graphite, the metallurgical testing done to date has firmly established Caula as being able to yield high percentages Super Jumbo, Jumbo and Large flakes.
The cumulative proportion of large to super jumbo flakes (>180m) averages 60% TGC for the combined Oxide Zone while the Fresh Zone averages 68% TGC giving a combined average for the Oxide Zone and Fresh Zone of 63% TGC.
This is a significantly better higher-value product distribution than all other peers in the Balama graphite province, including Syrah Resources.
A basket price of $1,103.50/tonne was calculated based on benchmark prices for the various flake sizes used in recent published peer group studies:
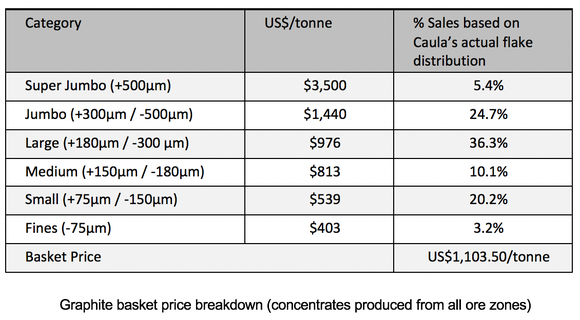
NXE believes this graphite basket price of $1,103.50, based on its flake size distribution and product specifications, to be saleable, especially when comparing its favourable graphite grade and flake size distribution against its East African peers.
Deal with major global commodities trader
What is highly encouraging is a major global commodities trader has given their support for funding of the project plus offtake.
NXE executed a confidentiality agreement with the trader which means they have likely been working through a dataroom for some time.
Due to the staged approach, the company has received a specific (non-binding and confidential) expression of interest from a major global commodities trader, confirming their interest to participate in the funding and off-take for Phase 1 and subject to the successful implementation of Phase 1 and receiving the off-take rights for Phase 2, to participate in and assist with arranging the funding for Phase 2 of the project.
Funding
NXE believes that it has reasonable grounds to assume that funding for the Caula project can be secured. The company has defined a clear strategy for funding of the different phases of the project and is confident that given the clear development and economic case presented in the scoping study it can be achieved.
Given the small initial pre-production capital expenditure for Phase 1 of approximately A$10 million the company is confident that funding can be obtained to proceed with Phase 1 with commissioning targeted for second half of 2019.
Following the successful operation of phase 1 for at least six months, NXE will need approximately US$77 million of external funds for phase 2 expansion.
NXE expect the most feasible way to achieve this via Export Credit Agency (ECA) project debt finance, which could account for up to 70% of the capital requirement and make it easier to raise the balance in equity finance from strategic investors and equity markets.
Decision to fast-track Caula proves warranted
Backed by rising vanadium and graphite prices and now armed with the scoping study that demonstrates that an open pit vanadium and graphite mining operation has ‘outstanding’ economics, NXE’s decision to fast-track Caula is hard to fault.
Now supported by the scoping study, the high grade of NXE’s Caula Graphite-Vanadium Project will enable the company to generate a top-quality product at a low cost, maximising margins and providing protection against price volatility.
The results indicate that the project can concurrently produce high-value vanadium products and a scoping study of the Caula project has been completed, confirming exceptional economics — notably the A$929 million NPV and 78% IRR.
There’s plenty in store for investors as the company continues to fast track progression of the project, including the subsequent pre-feasibility study (PFS) which will build on the scoping study results. This is targeted for release in the first half of 2019.
General Information Only
This material has been prepared by StocksDigital. StocksDigital is an authorised representative (CAR 000433913) of 62 Consulting Pty Limited (ABN 88 664 809 303) (AFSL 548573).
This material is general advice only and is not an offer for the purchase or sale of any financial product or service. The material is not intended to provide you with personal financial or tax advice and does not take into account your personal objectives, financial situation or needs. Although we believe that the material is correct, no warranty of accuracy, reliability or completeness is given, except for liability under statute which cannot be excluded. Please note that past performance may not be indicative of future performance and that no guarantee of performance, the return of capital or a particular rate of return is given by 62C, StocksDigital, any of their related body corporates or any other person. To the maximum extent possible, 62C, StocksDigital, their related body corporates or any other person do not accept any liability for any statement in this material.
Conflicts of Interest Notice
S3 and its associated entities may hold investments in companies featured in its articles, including through being paid in the securities of the companies we provide commentary on. We disclose the securities held in relation to a particular company that we provide commentary on. Refer to our Disclosure Policy for information on our self-imposed trading blackouts, hold conditions and de-risking (sell conditions) which seek to mitigate against any potential conflicts of interest.
Publication Notice and Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is current as at the publication date. At the time of publishing, the information contained in this article is based on sources which are available in the public domain that we consider to be reliable, and our own analysis of those sources. The views of the author may not reflect the views of the AFSL holder. Any decision by you to purchase securities in the companies featured in this article should be done so after you have sought your own independent professional advice regarding this information and made your own inquiries as to the validity of any information in this article.
Any forward-looking statements contained in this article are not guarantees or predictions of future performance, and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors, many of which are beyond our control, and which may cause actual results or performance of companies featured to differ materially from those expressed in the statements contained in this article. S3 cannot and does not give any assurance that the results or performance expressed or implied by any forward-looking statements contained in this article will actually occur and readers are cautioned not to put undue reliance on forward-looking statements.
This article may include references to our past investing performance. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of our future investing performance.

